Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Agrochemical Functions
- Cleaning Ingredients Functions
- Fluids & Lubricants Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
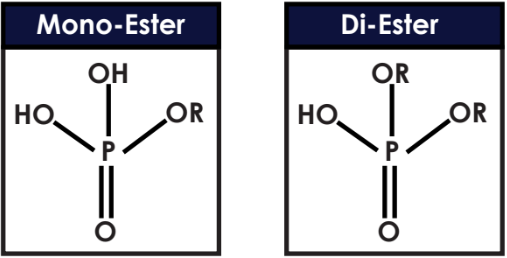
- Chemical Structure of Phosphate Esters
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Agrochemicals Features
- Fluids & Lubricants Features
- HII Features
- Background on Phosphate Esters
- Phosphate Esters are anionic surface active agents produced by reacting polyphosphoric acid or phosphorous pentoxide with molecules containing hydroxyl groups - commonly ethoxylated moieties or alcohols. Reactions using phosphorous pentoxide result in a mix of mono and di-esters, while products made with polyphosphoric acid are high in mono-ester yield.
- Which type to use depends upon the properties needed in formulation. Mixed esters products are generally better for emulsification; whereas, mono- ester rich exhibit better hydrotroping properties.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Fluids & Lubricants Type
- Fluids & Lubricants End Use
- Home Care Applications
- I&I Cleaning Applications
Properties
- Physical Form
- Soluble In
- Soluble in
- Water, Ethanol, Xylene
- Insoluble in
- Mineral oil, Kerosene
- Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Caustic Solubility (in 18% NaOH at 25°C) 17.3 - - Activity 99.0 % - Moisture Content max. 1.0 % - Pour Point max. 40 °F - Acid Value (at pH 5.5 - 9.5) 126 - 135 mg KOH/g - Weight (at 68°F) 9.4 lbs/gal - Surface Tension (at 0.05% Aqueous at 77°F) 30.7 dynes/cm - - SDS Physical and Chemical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Specific Gravity (at 25°C) 1.1 - - pH (at 5% in DI Wat er) 2 - 3 - - Boiling Point 213 °C - Freezing Point 42.35 °C - Appearance Clear - - Flammability Class Combustible iiib estimated - - Physical State Liquid - - Odor Mild - - Flash Point min. 100 °C Pensky Martens Closed Cup Explosive Limits Not explosive - - Oxidising Properties Not oxidizing - - Color Off-white to pale yellow - - Soluble in Water - -
Regulatory & Compliance
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
- Supplied by
